What is a VoIP PBX?
VoIP PBX also referred to as IP PBX, is a business telephone system that transmits phone calls over an IP network rather than through PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), or the traditional circuit-switched telephone network. VoIP PBX can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud (cloud-based PBX or hosted PBX).
Hosted VoIP PBX is known to be one of the most flexible and cost-effective business phone systems.
Some of the major benefits of using hosted VoIP PBX are:
- fewer maintenance costs
- lower call rates for domestic and international calls
- easy scalability
- increased mobility
- compatibility with different device types (desk phones, softphones, conference phones, and mobile devices)
- improved data security
- no need for in-house IT infrastructure
What is the difference between PBX and VoIP?
Both PBX (Private Branch Exchange) and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) are business phone systems that are used for achieving the same end goal – to make and receive phone calls. The difference between them lies in how they operate and their advantages and disadvantages.
PBX analog phone system is connected to a local Public Switched Telephone Network (PTSN) through a landline. It connects all office desk phones on the same network and allows making internal and external calls. It also offers several features that are not available on traditional phones (call transfers, IVR menu). PBX systems are considered reliable, secure, and provide high call quality, but the initial setup and maintenance costs are usually high.
VoIP phone systems convert analog phone calls into IP packets that are sent through the Internet. Though it’s a fairly recent technology in phone systems, it proves to be very flexible, easily scalable, and more cost-efficient than PBX. However, VoIP performance and the sound quality of calls may be affected by Internet outages and disruptions.
What is PBX compatible with?
A traditional PBX system uses physical phone lines and is compatible with analog phones (landline phones). PBX connects the phones and extensions within an organization to each other and outside analog lines. With a PBX system, a company can have more phones than phone lines. Though PBX systems traditionally used copper-based landlines, VoIP has changed the game. Today, a VoIP PBX (or IP PBX) is usually compatible with a range of SIP phones and softphones.
What is PBX hardware?
Traditional analog PBX phone systems connect to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) over Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) lines. A PBX system manages calls between phones and fax machines by being physically connected to them over copper wiring. The PBX phone system hardware is typically located in an office’s telecom closet or a server room. The hardware needs to be set up, configured, and maintained by a company’s IT staff. In the case of using hosted PBX systems, the PBX hardware is located off-site while the calls are routed to your phones over the Internet. A hosted PBX phone system is set up and maintained by the company housing the PBX hardware.
Does VoIP require a PBX?
VoIP functions independently and doesn’t require a PBX phone system in place to work efficiently. VoIP only needs an active Internet connection and a VoIP phone. Today’s VoIP service providers can offer businesses most PBX features without needing to have on-site PBX hardware. However, if you opt for on-premises IP PBX (VoIP-based PBX), the system would still require PBX. But instead of physically connecting to the PBX with copper wiring, phones connect to the PBX over the Internet.
How does the IP PBX phone system work?
IP PBX phone systems place and receive phone calls over the Internet instead of the traditional phone lines. The system converts analog voice signals into digital packets and then directs them to a VoIP service provider to manage each call’s initiation and termination. IP PBX is based on SIP standards and can be compatible with IP phones, mobile devices, and softphones. The IP PBX includes an index of all users, phones, and their corresponding SIP addresses.
When a user places a call, the PBX server can differentiate between internal and external calls. Internal calls are routed to the SIP address of the phone or user receiving the calls. External calls are routed through a VoIP gateway or a VoIP service provider to the desired destination.
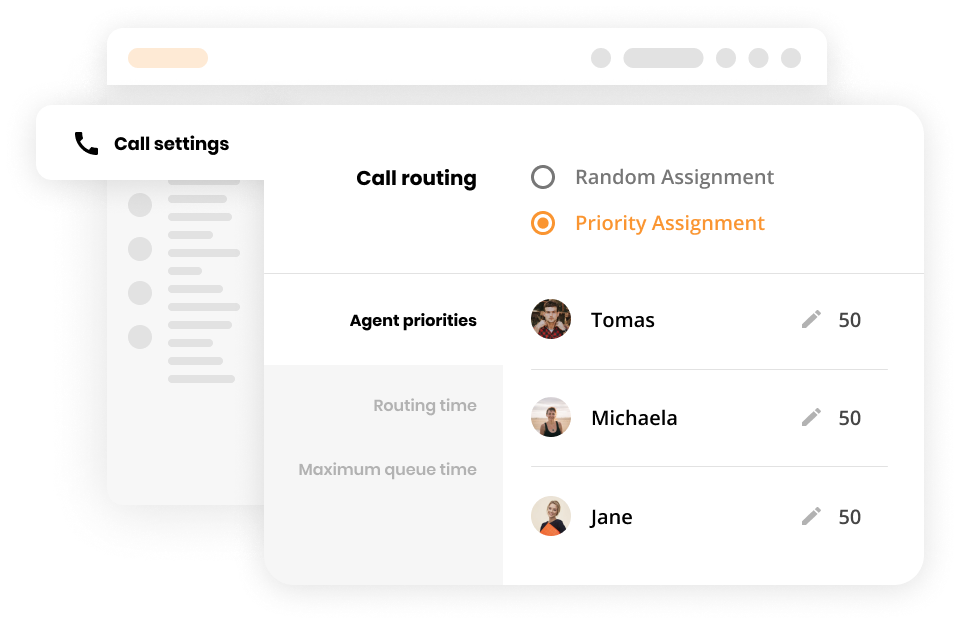
What is the difference between PBX and PABX?
While PBX is a ‘Private Branch Exchange’, PABX stands for a ‘Private Automatic Branch Exchange’. The difference between the two goes back to the history of phone systems. Originally, a PBX system required switchboard operators to manually connect internal callers to the right extension. That established a connection between two people using POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service). Eventually, PBX evolved into PABX when electronic switching became available. It enabled users to dial an extension number to make an internal call without needing an operator. Technically, since non-automatic PBXs don’t exist anymore, today’s PBX systems are PABX.
What is the PBX number?
A PBX number is a phone number that makes it easier for a company to organize incoming calls. With the help of a PBX number, companies collect all their incoming calls to one number and then transfer the calls to the right office, department, or people. A PBX number can be programmed to automatically transfer a call to another number when the first number does not answer or is busy.
VoIP service providers offer greater flexibility
Curious about VoIP and how it can give you the ability to make affordable calls?
Watch a video about VoIP PBX
The connection between Live Agent Helpdesk Software and a VoIP PBX (Private Branch Exchange) lies in their collaboration to streamline and optimize customer support operations. Live Agent Helpdesk Software enables businesses to provide real-time assistance and support to customers through various communication channels. A VoIP PBX, on the other hand, serves as a centralized system for managing phone calls within an organization. By integrating Live Agent Helpdesk Software with a VoIP PBX, businesses can enhance their customer support capabilities. Calls made to the helpdesk can be efficiently routed, queued, and distributed to available agents through the VoIP PBX, ensuring that customer inquiries are promptly addressed. This integration enables seamless communication, improved call handling, and better coordination between the helpdesk software and the VoIP infrastructure, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction and efficient support operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a VoIP PBX?
VoIP PBX is a business telephone system that utilizes VoIP technology. It differs from a traditional PBX system in that it transmits phone calls via IP networks rather than through circuit-switched telephone networks. VoIP PBX systems can be either on-premises or hosted (cloud-based).
What is the difference between PBX and VoIP?
PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a business phone system that is connected to a local PSTN through landline and allows employees to connect internally and externally. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) uses an Internet connection to make calls and is considered more flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient than a traditional PBX system.
What is PBX compatible with?
A traditional PBX system utilizes landlines wired by the telephone company. It is therefore compatible with landline phones only. However, a VoIP-enabled PBX system uses digital signals instead of analog ones and it’s usually compatible with a variety of SIP phones and softphones.
What is PBX hardware?
Traditional analog PBX phone systems use copper-based landlines and hardware that is physically located in a company’s telecom closet or a server room. The PBX hardware is set up, configured, and maintained in-house. With hosted PBX systems that run using an Internet connection, the PBX hardware is located off-site and managed by the company housing the hardware.
Does VoIP require a PBX?
VoIP phone systems do not require PBX to operate. You would only need a high-speed broadband internet network connection and a VoIP phone to get started. A typical VoIP provider can offer a range of PBX capabilities without needing to have in-house PBX hardware.
How does IP PBX work?
The IP PBX phone system works over the internet instead of using traditional phone lines. The system operates by converting analog voice signals into digital packets and directing them to a VoIP service provider to coordinate the initiation and termination of calls.
What is the difference between PBX and PABX?
PABX (Private Automatic Branch Exchange) has become the evolution of traditional PBX systems that required switchboard operators to manually connect calls between extensions. PABX automated the whole process when the electronic switching technology was adopted.
What is the PBX number?
A PBX number helps companies organize their incoming calls by collecting all inbound calls to one number and transferring them to the right people or departments. A PBX number can be configured to transfer a call to another number in case the first number is busy or not answered.
After diving into the ins and outs of VoIP PBX, you might be curious about how the software behind it works. The VoIP software page explains the features and benefits of using VoIP over traditional phones, and it's a great next read if you're considering a transition. Also, if you're on the go, learning about Mobile VoIP can be beneficial. Discover how mobile VoIP technology works and its various applications in enhancing communication flexibility.
The best free call center software
Experience seamless customer support with LiveAgent's free call center software. Unlimited recordings, no setup fee, and 24/7 service!
20 Best VoIP phone systems and integrations
Explore the top 20 VoIP phone systems and integrations for 2024 to enhance your business communications. Learn how to choose the best VoIP solution based on features, pricing, and requirements to streamline operations effectively. Discover the benefits of VoIP technology and find the perfect fit for your company's needs.
Discover seamless communication with Voxtelesys and LiveAgent integration. Enhance your business connectivity with reliable SIP Trunking, Cloud PBX, and SMS services at no extra cost. Voxtelesys offers superior VoIP solutions, ensuring crystal-clear calls and robust security. Start your free trial today!
Leading softphone software for B2B & B2C businesses
Discover LiveAgent's top-rated softphone software for B2B & B2C businesses, offering SIP-based VoIP support for seamless, reliable communication from anywhere. Enjoy features like call routing, IVR, unlimited recordings, and more. Start your free trial today and elevate your customer service with ease!

 Български
Български  Čeština
Čeština  Dansk
Dansk  Deutsch
Deutsch  Eesti
Eesti  Español
Español  Français
Français  Ελληνικα
Ελληνικα  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Italiano
Italiano  Latviešu
Latviešu  Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai  Magyar
Magyar  Nederlands
Nederlands  Norsk bokmål
Norsk bokmål  Polski
Polski  Română
Română  Русский
Русский  Slovenčina
Slovenčina  Slovenščina
Slovenščina  简体中文
简体中文  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  العربية
العربية  Português
Português